Energy Distribution is central to modern life. The operation of everything from the lights in our homes to large industrial machinery depends on a stable supply of energy. Energy Distribution plays a significant role in ensuring this supply. Starting from power plants, this process must reach the end-user safely, efficiently, and in a controlled manner. Therefore, Energies Distribution is divided into different systems based on voltage levels, areas of use, and technological infrastructure. In this article, we will examine the types of Energies Distribution in detail.
What is Energy Distribution?
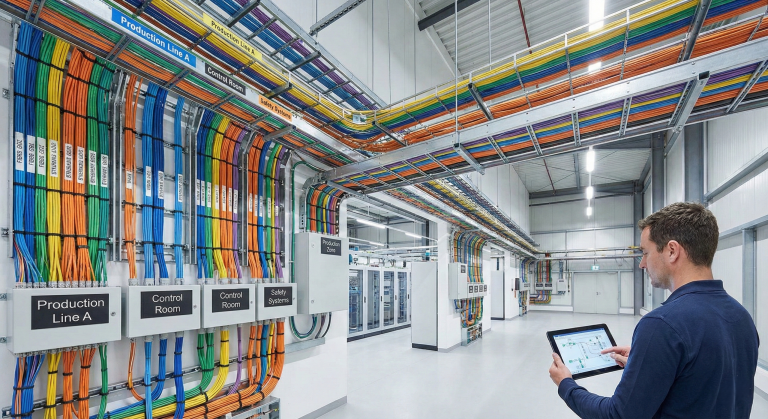
First, let’s define the concept: Distribution refers to the process of taking electricity from production points and delivering it to consumption points. This system is not just about transmission lines. It includes numerous technical components such as transformer substations, panel systems, cabling infrastructure, and protection systems.
In a modern Energy Distrbution system, safety, sustainability, and energy efficiency are fundamental goals. Engineering solutions based on needs analysis are essential, regardless of the type of distribution used.
How are Energy Distribution Systems Classified?
Energy Distribution is generally categorized according to voltage levels. These levels are determined by considering both the area of use and the transmission distance. Generally, the systems are grouped under three main headings:
- Low Voltage (0-1kV)
- Medium Voltage (1kV-36kV)
- High Voltage (Above 36kV)
This classification allows for the development of specific solutions for each type of structure. Now, let’s take a closer look at these three basic structures.
1. Low Voltage Energy Distribution
Low voltage Energy Distribution is one of the most commonly used systems. It is generally preferred in residential areas, small businesses, schools, and neighborhood networks. The voltage in these systems is usually between 220-400V. Cables are thinner, and distribution panels have a simpler structure. These systems, which are easier to control in terms of safety, are user-friendly and have lower maintenance costs.
Energy Distribution at this level is carried out through local distribution companies. It is particularly widespread in urban settlements.
2. Medium Voltage Energy Distribution
Medium voltage Distribution typically operates at voltage levels between 1kV and 36kV. It is preferred in factories, hospitals, shopping centers, logistics facilities, and organized industrial zones. In systems carrying energy at this level, transformer substations are of critical importance. Distribution is optimized through transformers specifically positioned for each facility.
Panel and cabling products used in medium voltage systems must be more durable and high-performance. Safety equipment is advanced, and insulation technologies are stronger. Distribution becomes more complex at this level, and engineering support becomes mandatory.
3. High Voltage Energy Distribution
High voltage systems generally cover levels above 36kV. This type of Energy Distribution is used over long distances between the production point and distribution regions. For example, tasks such as transmitting energy from a hydroelectric power plant to a city belong to high voltage systems.
Overhead lines, steel poles, underground cables, and high-performance transformer stations are components of this system. High voltage Energy Distribution is preferred to minimize energy losses during transmission. At the same time, maintenance, inspection, and monitoring systems must also be very advanced.
New Generation Energy Distribution: Microgrids and Renewable Systems
The transformation in the energy sector has also been reflected in distribution systems. Now, not only energy from central production but also locally generated energy from renewable sources is coming into play. Thanks to micro-generators such as solar panels, wind turbines, and biogas plants, distribution systems are increasingly operating with a microgrid logic.
In this new system, Energy Distribution becomes much more flexible. Production and consumption can be achieved at the neighborhood level. This reduces the load on central systems and increases sustainability.
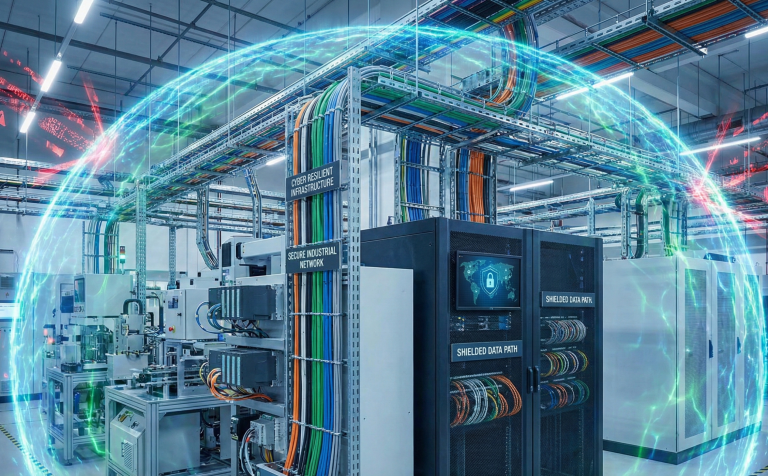
The Importance of Energy Distribution in Industrial Facilities
Correct Energy Distribution in industrial areas directly affects the efficiency of production. Proper placement of panels, optimization of cable routes, and installation of backup systems reduce failures while increasing efficiency. The support of expert companies is very valuable here.
For example, Delta Tema offers maximum safety and sustainability in Energy with its high-quality panel solutions and cable carrying systems for industrial facilities. Thanks to systems manufactured in accordance with local and global standards, energy interruptions are minimized.
Safety and Legal Standards in Energy Distribution
Safety should never be neglected in the Energy Distribution process. Residual current protection systems, grounding arrangements, fuse systems, and insulation technologies must comply with standards. In Turkey, TSE, and internationally, IEC and ISO standards are decisive in this field.
Conclusion: Future-Proof Energy Distribution Strategies
Energy Distribution is one of the fundamental building blocks of technological infrastructure. While low, medium, and high voltage systems address different needs, new generation microgrid structures have taken their place among the solution alternatives of the future.
Having the correct Distribution system for every structure, from industrial zones to individual residences, brings not only efficiency but also safety. Working with expert companies in the field, such as Delta Tema, ensures that this process is healthier and more sustainable.