Electricity, Energy, and Wiring: The Foundations of Modern Life
Electricity and energy are the cornerstones of modern life. From lighting up cities to powering industrial facilities, electrical energy plays a vital role in every aspect of life. The safe and efficient transmission and distribution of this energy are made possible by wiring systems. Proper and high-quality wiring in electrical systems is crucial for both safety and energy efficiency. In this article, we will explore the fundamental principles of electricity, energy, and wiring, as well as their importance in the modern world.
Fundamentals of Electricity and Energy
Electrical energy is essential for a wide range of applications and devices in daily life. The sources of electrical energy typically include fossil fuels, nuclear energy, and renewable energy resources. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are extracted from the earth, while nuclear energy is produced through the splitting of radioactive materials like uranium. Renewable energy sources include natural resources such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and biomass energy.
Production and Transmission of Electrical Energy
Electrical energy is generated using generators, which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. These devices operate in various ways, such as through water movement in hydroelectric plants, steam turbines in thermal power plants, or wind turbines in wind power plants. The generated electrical energy is delivered to consumers via transmission lines and cable systems.
Types of Wiring and Their Applications
Electrical cables are manufactured in various types to suit specific purposes and needs. Here are the main cable types and their applications:
- Power Cables: Used for transmitting electrical energy, they have a high current-carrying capacity. They are usually made of copper or aluminum and coated with insulation materials.
- Control Cables: Used in control and command circuits of electrical systems. Due to their fine, flexible structure, they are widely used in electronic device control circuits.
- Data Cables: Used in computer networks and telecommunications systems for data transmission. Fiber optic cables are ideal for high-speed, long-distance data transmission.
Technical Details of Wiring
When installing wiring in electrical systems, certain technical details must be considered to ensure safety and efficiency:
- Proper Installation: Cables must be installed securely and safely to prevent potential malfunctions. They should be protected from unnecessary tension and mechanical damage.
- Insulation and Grounding: Proper insulation and grounding of cables are essential to prevent electrical leaks. Grounding is particularly crucial for high-voltage systems.
- Cable Trays: Cable trays should be used to organize and protect cables systematically. These trays ensure easy accessibility and facilitate maintenance when needed.
Safety Measures
Here are some critical safety measures to follow during electrical wiring:
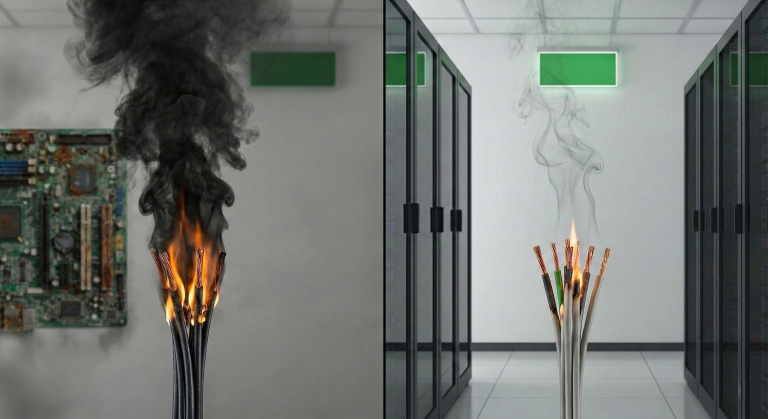
- Short Circuit and Overload Protection: Protective devices, such as fuses and circuit breakers, should be used to prevent damage to cables in case of short circuits or overloading.
- Fire Safety: Fire-resistant cables should be chosen to minimize fire risks. Additionally, fire detectors and extinguishing systems should be installed in areas where cables pass through.
- Periodic Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance of cables ensure the early detection of potential faults, guaranteeing the safe and uninterrupted operation of the system.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Today, energy efficiency and sustainability have become top priorities in electrical and wiring systems. Energy-efficient wiring systems minimize energy losses and reduce environmental impacts. Additionally, integrating renewable energy sources enhances the sustainability of energy systems.
- Renewable Energy and Wiring: Renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, require proper wiring systems during integration. The cables used in these systems must be durable and long-lasting, capable of withstanding environmental conditions.
- Energy Conservation: Energy-efficient devices and systems help save energy, reducing both costs and environmental impacts.